|
|
Green Energy Cellulose (Chongqing) Technology Co., Ltd.PHONE:023-62593599 E-MAIL:gecm@sanjiagecm.com URL: www.gecm.com.cn ADD:No. 22, No. 73, Hongguang Avenue, Huaxi Street, Banan District, Chongqing |
|
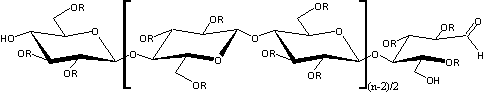
Research and application of natural cellulose-based pharmaceutical excipientsThe molecular structure of natural cellulose is a linear homopolymer in which 1-5 of D-glucopyranose anhydrides are connected with each other by b-1,4 glycosidic bonds, and it is a semi-rigid polymer. The three alcoholic hydroxyl groups on the glucose residue ring can undergo oxidation, esterification, etherification and other reactions to obtain various cellulose ethers and ester derivatives, which are widely used in medicine for thickening, excipients, sustained release, controlled release, forming film, etc. Its general structural formula can be simplified as follows:
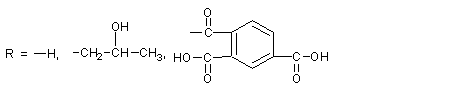
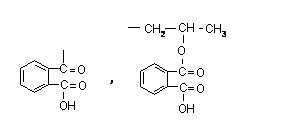
Because of its wide range of raw materials and good compatibility with human body and environment, it has received great attention. This article reviews the natural cellulose and its derivatives that are used in pharmaceutical excipients, and expounds their respective structures and their functions as pharmaceutical excipients. 1. natural cellulose ester Cellulose esters are the product of the esterification of hydroxyl groups in cellulose. 1.1 Cellulose acetate [1] (CA) CA is partially acetylated cellulose, in the general structural formula, R= -COCH3 or -H, which contains acetyl (CH3CO-) 29.0%~44.8% (W/W), that is, each structural unit is about 1.5 ~3.0 hydroxyl groups are acetylated with a residual free acetic acid content of no more than 0.1%. The addition of acetyl groups in the CA molecule only retains a small amount of hydroxyl groups, which reduces the regularity of the molecular structure, reduces the hygroscopicity, and improves the heat resistance. In medicine, cellulose mono- or diacetate is often used for film coating, which is white powder with a specific gravity of 1.33. ~1.36, easily soluble in acetone and ethanol. For cellulose acetate, it can be used as a coating material for acetaminophen, theophylline, etc. Dissolving cellulose acetate in acetone/ethanol mixture, spray coating, and adjusting the composition of coating materials, different drug release rates can be obtained. In the sustained release of active drugs, the drug is often interspersed in the hydrophobic matrix, and the role of the drug matrix material is to limit the exposure of the active drug to gastric or intestinal fluid, so as to inhibit the diffusion of the active drug in the matrix. The parent material is required to have low toxicity, or be inert in gastric juice and intestinal juice, and CA with a degree of substitution of about 2.5 is a good parent material. CA, active drug and other excipients can be uniformly mixed and compressed to form a medicament. This process compresses both hydrophilic and hydrophobic polymers to the matrix. Masih et al. [2] successfully prepared a sustained-release matrix interspersed with highly active drugs by a mixed-pressure method using CA. Guyonnet et al. [3] found that active tablets such as theophylline can be interspersed in the mixed matrix of CA and phosphate to achieve sustained release pharmaceutical purposes. Fengl et al. [4] found that even according to the 12:1 mixed system of active drug and cellulose acetate, the release of theophylline could be inhibited by the parent; as the content of theophylline in the mixed system decreased, the release rate increased. The drug release rate is not completely dependent on the molecular weight of CA, but also has a great relationship with the type and amount of plasticizer. 1.2 Aliphatic mixed cellulose ester[5] Cellulose acetate propionate (CAP-482-20), in the general structural formula, R= -COCH2CH3 or -H, cellulose acetate butyrate (CAB-381-0.5), in the structural formula of Figure 2, R= -COCH2CH2CH3 or -H, the parent body that can also be prepared by the method used by CA has good mechanical properties. There is also cellulose acetate succinate (CAS), in the structural formula, R = --COCH2CH2COOH or -H, due to the large distance between ionized carboxyl groups, large pKa, weak acidity, and only swelling at pH 6.5. The precursor can be prepared by controlled sedimentation of the polymer in a solution in which the active drug is dispersed. This detailed method for preparing the precursor is described in Belgain's patent [6]. First, CAB is mixed with theophylline dispersed in a non-solvent liquid (such as stearate-containing inorganic oil), then the mixture is emulsified in acetone, and the acetone in the mixture is removed by vacuum drying for granulation. A polymer matrix with embedded active drug was made. 1.3 Aromatic mixed cellulose esters Cellulose acetate phthalate (CAP) is a phthalate ester of partially acetylated cellulose. In the structural formula, R=-COC6H4COOH, -COCH3 or -H, which contains acetyl (CH3CO) 19.1%~23.5%, phthalate The acyl group is 30.0%~36.0%, and the free phthalic acid does not exceed 0.6%. It is formed by esterification of cellulose acetate and phthalic anhydride. CAP is a white fibrous powder, insoluble in water, ethanol, hydrocarbons and chlorinated hydrocarbons, but soluble in acetone or acetone/ethanol mixture. Under the condition of high temperature and high humidity for a long time, slow release and decomposition will occur, thereby increasing the content of free acid and changing the viscosity to affect the use. The pH value of its dissolution is about 5.5. The standard coating liquid configuration requires that the mass content of CAP powder is 8%~10%, and the content of plasticizer dissolved in acetone is 20%~30%. When coating, 8%~12% acetone-ethanol mixed solution is generally used, which has good film-forming properties and is easy to operate. The coated tablet is insoluble in acid solution but dissolved in buffer solution with pH 5.8~6.0, and trypsin can promote its digestion. As an enteric coating material, CAP is generally added with diethyl phthalate as a plasticizer. Due to the need to add an organic solvent, its volatilization pollutes the environment, and is flammable and explosive. El-Said and Hashem [7] found that the disintegration time of theophylline and its derivatives tablets will be delayed due to the presence of CAP in the system after direct mixing. This delay time is directly related to the content of CAP. Relationship. They performed dissolution experiments using buffer solutions of 0.1N HCl and pH 7.4 phosphate, and found that drug release was significantly inhibited in both solutions. China has rarely used CAP, but it is still used abroad, and its water dispersion has been developed, which overcomes the shortcomings of using organic solvents to pollute the environment, which is flammable and explosive. Cellulose acetate trimellitate (CAT) is a trimellitate of partially acetylated cellulose. Compared with CAP and CAS, the distance between ionized carboxyl groups is the smallest, the pKa is small, and the acidity is the strongest. value dissolves. The test results show that CAP with different group contents dissolves at pH 5.5~6.5, the distance between ionized carboxyl groups of CAT is the smallest, the pKa is small, and the acidity is the strongest, and it dissolves at pH 5.0~5.5. CAS is the weakest acidity and only swells at pH 6.5. Cellulose esters play a key role in enteric coatings, hydrophobic matrices and semipermeable membranes for controlled drug delivery. 2. Cellulose ethers Cellulose ethers are made from alkali fibers The experimental results show that the methoxyl substitution degree of HPMCT is 1.7~2.1, the trimellityl group substitution degree is 0.2~0.5, and the dissolution pH value of the product is 3.5~4.5, but the substitution degree of trimellityl group is low (<0.2). When the hydrophobicity is insufficient, it does not have sufficient acid resistance, and moisture easily enters the enteric (>0.52) coating material. 3.3 Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate (HPMCAS) HPMCAS is the mixed ester of acetic acid and succinic acid of HPMC, which is obtained by esterification of HPMC with acetic anhydride and succinic anhydride. The product is washed and dried into powder. In the general structural formula, where R=-H, -CH3, -COCH3, -(CH2CH(OH)CH3)n, -CH2CHCH3, -CH2CHCH3, -COCH2CH2COOHOCOCH3 OCOCH2CH2COOH HPMCAS white to yellowish white powder, odorless, with acetic acid odor; soluble in sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate test solution, easily soluble in acetone or dichloromethane/ethanol (1:1) mixture, insoluble in water and ethanol And ether, can be dissolved in buffer solution within 10min, the pH range of its dissolution is 5.5~7.1. Thermal stability is better than CAP, HPMCP, can be used in water dispersion system. HPMCAS is a tablet enteric coating material, sustained-release coating material and film coating material developed in the 1970s and approved for application in the 1980s. In addition to enteric coating, it can also be used as a polymer carrier to prepare drug microcapsules, microspheres and drug sustained or controlled release preparations. Those whose particle size is below 5mm can also be used as water dispersion for coating. Animal experiments have proved that HPMCAS is safe and non-toxic when taken orally. Its special advantage is that it has good solubility in the upper part of the small intestine (duodenum), and is ideal for increasing the small intestinal absorption of drugs than some current enteric-coated materials. According to the results of this laboratory, the tensile strength of the free film without plasticizer reaches 45~55MPa, and the elongation at break reaches 6%~10%. The viscosity and mechanical properties of the free film show that it can replace HPMC and HPMCP as enteric coating materials in medicine. 3.4 Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate phthalate (HPMCAP) Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate phthalate (HPMCAP) is a mixed ester of acetic acid and phthalic acid of HPMC. It is an enteric coating package with excellent performance obtained by esterification of HPMC with acetic anhydride and phthalic anhydride. clothing material. In addition to enteric coating, it can also be used as a polymer carrier to prepare drug microcapsules, microspheres and drug sustained or controlled release preparations. As an enteric coating material, it is characterized by good film-forming properties and does not require plasticizers; it has good solubility in the upper part of the small intestine (duodenum), and is ideal for increasing the intestinal absorption of drugs than some current enteric-coated materials. Varieties of excipients that are in urgent need of development and application. In the general structural formula, where, R=-H,-CH3,-COCH3,-[CH2CHOHCH3]n,
The analysis results of the self-made products show that the cellulose derivatives have good film-forming properties, the tensile strength of the free film without plasticizers reaches 40~45MPa, and the elongation at break reaches 8%~10%. It can be well dissolved in solvents such as /dichloromethane, acetone/ethanol/water, and can replace HPMC and HPMCP as enteric coating materials in medicine. 4 Conclusion As mentioned above, there are many kinds of cellulose-based pharmaceutical excipients, and my country is still in the primary stage in terms of production and application, and it has reached a critical stage to strengthen its preparation and production, performance research and application research. |